Overview of lead-zinc ore resources and distribution at home and abroad
Release time:
2017-01-06 00:00
Lead and zinc are widely distributed on the earth, mainly in the form of sulfide and sulfate, with sphalerite and galena being the most important. Lead and zinc are mainly used in machinery, metallurgy, electricity, military industry, chemistry, medicine, light industry and other industries. They are widely used nonferrous metal elements [1]. Based on the collection of relevant data and information, this paper gives a basic overview of the resources and distribution of major lead-zinc mines in the world and China. Through the analysis of resource potential, it provides some suggestions for promoting the exploration, development and research related to lead-zinc resources
1 Overview of world lead-zinc resources
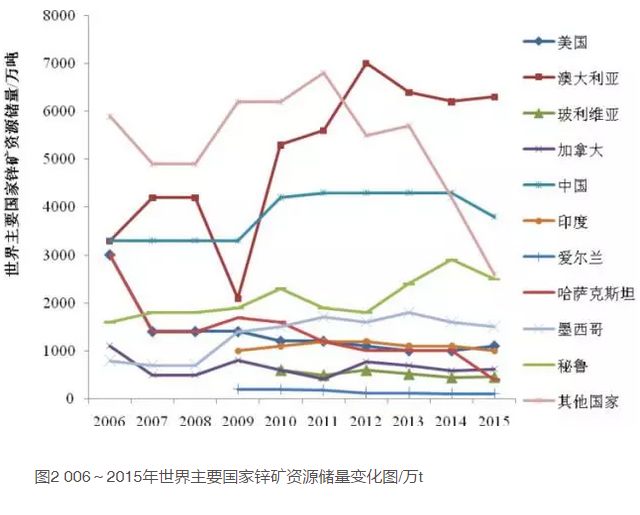
Lead and zinc resources are widely distributed in the world, and are known to be distributed in more than 50 countries [2]. According to the statistical data of USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (2007~2016) [3], by the end of 2015, the world's identified lead resources had exceeded 2 billion tons, and the Lead reserves were 89 million tons (Table 1, Figure 1); The zinc resource is 1.9 billion tons, and the zinc reserve is 200 million tons (Table 2 and Figure 2). The world's lead and zinc ores are mainly distributed in Oceania, Asia, North America and South America. Countries with large lead and zinc reserves include the United States, Australia, Bolivia, China, Peru, Mexico, India, Kazakhstan, Canada, Russia and Ireland, which together accounted for about 80% of the world's lead and zinc reserves in 2015. Among them, Australia has the richest lead and zinc mineral resources in the world, with lead reserves of 35 million tons, accounting for 39.32% of the world's total lead reserves, zinc reserves of 63 million tons, accounting for 31.50% of the world's total zinc reserves, and lead and zinc reserves of 33.91% of the world's total reserves
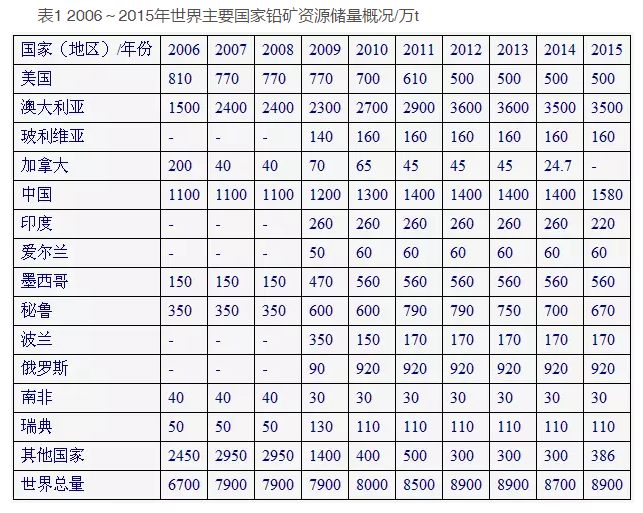
The data is quoted from USGS: Mineral Commodity Summaries 2007-2016 [3], where&ldquo-& rdquo; It means no data, and the world total is rounded
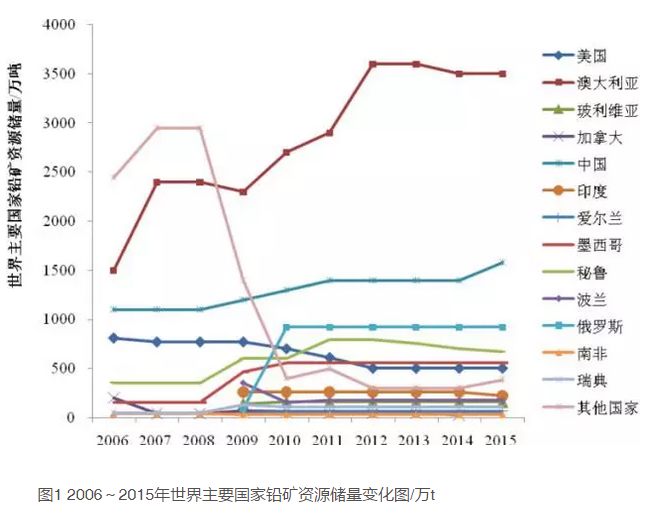
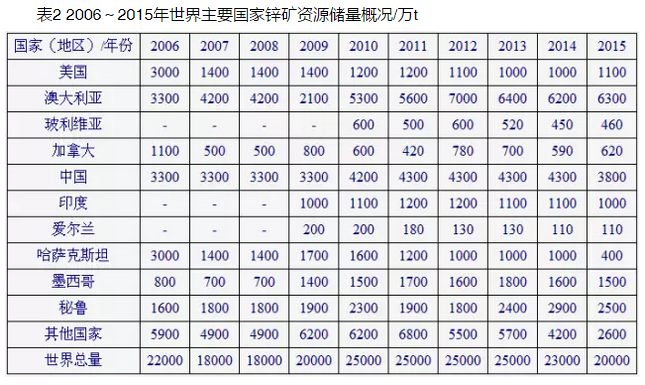
The data is quoted from USGS: Mineral Commodity Summaries 2007-2016 [3], where&ldquo-& rdquo; It means no data, and the world total is rounded
2. Distribution characteristics of lead-zinc resources in the world
According to statistics [2,4-7], there are 58 super giant lead-zinc deposits (5 million tons of lead+zinc original metal reserves>) worldwide (Figure 3), mainly distributed in Australia (10), the United States (7), Canada (6), China (5), Kazakhstan (4) and other countries. The genetic types of the deposits are mainly MVT type, Sedex type, pyrite type, gravel (shale) type, accounting for about 85% of the world's total lead and zinc reserves, followed by hydrothermal vein type, porphyry type, skarn type, etc
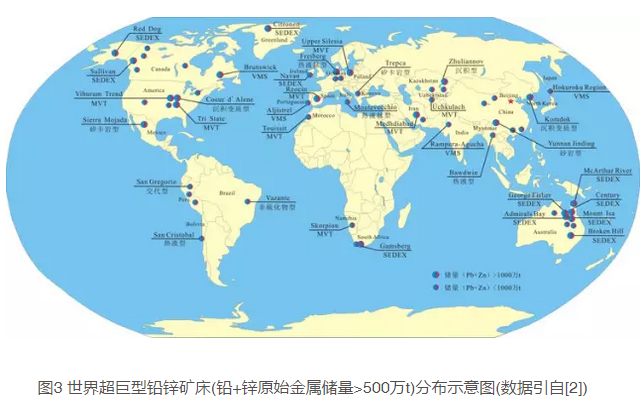
Lead zinc ore concentration area in Australia: ① McArthur River at the east edge of Barton Trough area, with a reserve of 25.8 million tons and an average grade of Pb+Zn of 13.6%; ② The lead and zinc reserves in the Broken Hill ore concentration area are at least 55 million tons, and the average grade of Pb+Zn is 25%; ③ Mount Isa has at least 6 giant large polymetallic ores, with a lead and zinc reserve of 11.69 million tons and an average grade of Pb+Zn of 13.2%; ④ At least 4 large lead-zinc deposits have been found in the Reed volcanic rock metallogenic belt of Tasmania Island, with lead and zinc reserves of 8.6 million tons
North American lead-zinc ore concentration area: ① Northwest Alaska, USA; Red Dog” Red Dog: Pb reserves are 6.67 million t, average grade is 4.3%, Zn reserves are 24.95 million t, average grade is 16.1%; ② The United States Kerdaran silver lead zinc ore belt (CoeurdAlene) has lead and zinc reserves of more than 10 million tons, and the average grade of Pb+Zn is 11.8%; ③ The lead-zinc ore concentration area in North America also includes the Mississippi River; ④ Kidd Creek deposit in Canada has lead and zinc reserves of 9.52 million tons, and the average grade of Pb+Zn is 6.42%; ⑤ Sullivan, Canada, has lead and zinc reserves of more than 20.83 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 11.9%; ⑥ The Selwin Basin in Yukon, Canada, has 900 million tons of lead and zinc ore reserves; Howard Pass in the east of the basin has a lead and zinc reserve of 8.5 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 7.7%; ⑦ More than 30 deposits have been proved in the Bathurst Newcastle ore concentration area in Appalachia, Canada, of which the lead and zinc reserves of Brunswick No. 12 deposit exceed 10.7 million tons, and the average grade of Pb+Zn is 13%; There are more than 100 deposits in Newfoundland Island ore belt, mainly medium and small ones, of which Buchans deposit has 234000 tons of Pb reserves with an average grade of 1.3%, and 1.08 million tons of Zn reserves with an average grade of 6%; ⑧ Crandon deposit in Subirir structural area has a zinc reserve of 3.9 million tons with an average grade of 6.5%; ⑨ The FlinFlon deposit in Amisk ore belt has a zinc reserve of 2.48 million tons and an average grade of 4.25%
South American lead and zinc ore concentration area: ① Peru San Gregorio metasomatic deposit (San Gregorio) has a lead and zinc reserve of 6.93 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 9.52%; ② The Antamina skarn deposit in Peru has a lead and zinc reserve of 5.75 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 10.3%. ③ The lead and zinc reserves of the San Cristobal hydrothermal deposit in Bolivia are 5.49 million tons, and the average grade of Pb+Zn is 2.12%; ④ The lead and zinc reserves of Brazil's Vazante non sulfide deposit (Vazante) are 5.13 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 18%
Central Asia lead and zinc ore concentration area: the lead and zinc deposits in Central Asia are mainly concentrated in Kazakhstan, and there are mainly three metallogenic belts. ① There are many large polymetallic deposits distributed in the Altay copper lead zinc metallogenic belt, among which the Leninogorsk deposit has a lead and zinc reserve of 3.8 million tons, and the grade of dense massive ore: Pb 15.2%, Zn 28.8%; Grade of disseminated ore: Pb2.5%, Zn 5.1%; The lead and zinc reserves of Jiliannov ore field (Zhuliannov) are more than 5 million tons, and the primary ore grade is: Pb 1.7%, Zn 2.9%; ② More than 10 lead-zinc deposits have been found in the eastern Zhungeer Alatao metallogenic area, one of which is 150km long and 20-50km wide. The Czech deposit has a lead-zinc reserve of 5.5 million tons, and the average grade of Pb+Zn is 11%; ③ Kalatao polymetallic metallogenic belt at the southwest edge is 600km long and tens of kilometers wide, with several important deposits, including Shalkya super large lead-zinc deposit, with a lead and zinc reserve of 12.39 million tons and an average grade of Pb+Zn of 4.13%
East Asia lead and zinc ore concentration area: ① Korean Cende lead and zinc ore field (Komdok), with lead and zinc reserves of 70 million tons, and the average grade of Pb+Zn of 7%~10%; ② Jinding Lead Zinc Mine, Yunnan, China, has a lead and zinc reserve of 16.1 million tons, with an average Pb+Zn grade of 8.44%; ③ The MVT lead-zinc mine in Fankou, Guangdong, China, has lead and zinc reserves of 8.29 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 14.01%; ④ Changba lead-zinc ore field, Gansu, China, has a lead and zinc reserve of 7.92 million tons, with an average Pb+Zn grade of 8.46%; ⑤ Dongshengmiao Lead Zinc Mine, Inner Mongolia, China, has lead and zinc reserves of 6.26 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 3.25%; ⑥ Hokuroku Region, Japan, has a lead and zinc reserve of 6.63 million tons, with an average grade of Pb+Zn of 6.5%
3 Overview of China's lead-zinc ore resources
China is rich in lead and zinc metal resources. According to the data of China Mineral Resources Report (2015) [8], by the end of 2014, the amount of lead metal and zinc metal identified nationwide had reached 73.849 million tons and 144.861 million tons, respectively, an increase of 9.6% and 5.5% compared with 2013 (Table 3, Figure 3). The lead and zinc mineral resources in China are characterized by many ore occurrences and scattered resources. Since 1994, when China became the second largest lead and zinc producer in the world, with the rapid development of the national economy, the demand for lead and zinc resources has also been increasing. However, with years of mining, most of the mine resources have been gradually exhausted, and the output has declined year by year. In the face of the increasingly prominent contradiction between supply and demand of lead and zinc minerals, how to achieve a breakthrough in prospecting as soon as possible has become a major mission of geological work under the new situation. In the past decade or more, the government has also attached great importance to the prospecting work, and implemented such special prospecting work as the National Special Project for the Exploration of Successive Resources of Crisis Mines and the Demonstration Project for the Deployment and Demonstration of Land and Resources Survey. With the rapid development of geological technology and theory, the joint exploration of new technologies and methods, deep prospecting has become possible, and has become the only way to achieve a breakthrough in prospecting. The results of special prospecting work show that deep prospecting has achieved remarkable results, demonstrating China's huge prospecting potential [1]
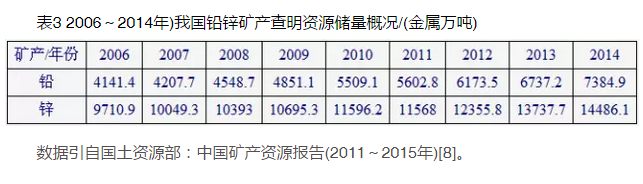
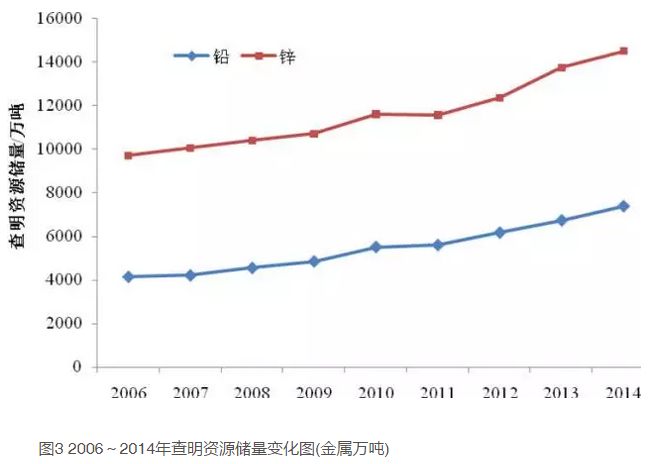
The main characteristics of lead-zinc ore resources in China are as follows: ① There are more small mines than large ones. Large lead deposits only account for 1.5% of all lead deposits, and large zinc deposits account for 4.5% of all zinc deposits. ② There are many poor ores and few rich ores. The lead resource reserves (331) with a grade of more than 3% only account for about one-third of the total lead resource reserves (331). The zinc ore grade is relatively high, but the deposits with a zinc ore grade of less than 4% still account for more than 35%. ③ The recoverable life of lead and zinc reserves and their basic reserves is slightly insufficient, with lead reserves less than 4 years and zinc reserves less than 5 years; The basic lead reserves are 5.6 years and the basic zinc reserves are 7.4 years. The reserve resources are relatively scarce, and the reserves of resources available for planning and utilization are insufficient. ④ China's lead and zinc industry related mines are mainly small and medium-sized enterprises. ⑤ With the rapid development of lead and zinc smelting capacity in China, the import of lead and zinc raw materials has also increased rapidly
4. Distribution characteristics of lead-zinc ore resources in China
Lead zinc ore is one of the dominant mineral resources in China. China's lead and zinc mines are mainly distributed in Guangdong, Guangxi, Hunan, Yunnan, Sichuan, Gansu, Xinjiang, Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia and other provinces (regions). Important mineral deposits mainly include Guangdong Fankou, Guangxi Dachang, Jiangxi Lengshuikeng, Jiangsu Qixia Mountain, Hunan Shuikou Mountain, Yunnan Jinding, Sichuan Daliangzi, Gansu Changba, Xinjiang Hoktale, Qinghai Xitie Mountain, Inner Mongolia Dongsheng Temple, etc; The production areas of lead-zinc ores are relatively concentrated in Nanling, Sanjiang and Qinling Qilian Mountains